Hello guys, if you are wondering how to create Microservices in Java then you have come to the right place. Microservices architecture has gained significant popularity due to its
scalability, modularity, and ease of deployment. When it comes to building
microservices, gRPC (Google Remote Procedure Call) is an excellent choice for
facilitating communication between services. In last few articles, I have shared how to build Microservices in Java using Spring Boot and How to build Microservices app using Quarkus and In this article, we will explore
how to create a microservice application using gRPC in Java, along with a
comprehensive step-by-step tutorial.
How to create a Microservice application using gRPC in Java? Along With Example Tutorial
Now, let's see step by step how to build Microservices application using Google's gRPC technology:
What is gRPC?
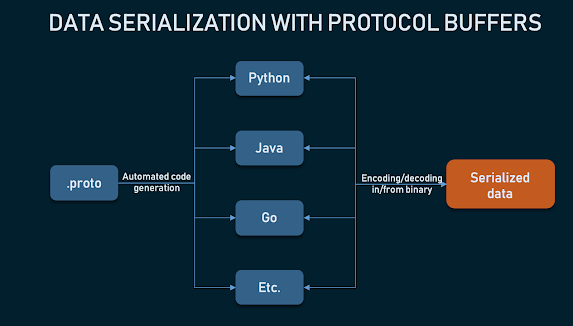
gRPC is a high-performance, open-source framework developed by Google for
building efficient and scalable microservice applications. It uses the
Protocol Buffers (protobuf) language-agnostic binary serialization format
for defining service interfaces and message types, allowing for
language-independent communication between services.
Step-by-Step Tutorial: Creating a Microservice Application with gRPC in
Java
To demonstrate the process of building a microservice application using gRPC
in Java, we will create a simple example of a user management system with
two microservices: a User Service for user CRUD operations and an
Authentication Service for user authentication.
Prerequisites:
Java Development Kit (JDK) installed (version 8 or higher).
Apache Maven installed.
Step 1: Define the gRPC Service and Message Types:
Start by defining the service and message types using Protocol Buffers.
Create a new file called user.proto and define the following:
syntax = "proto3";
package com.example.usermanagement;
service UserService {
rpc CreateUser(CreateUserRequest) returns (UserResponse) {}
rpc GetUser(GetUserRequest) returns (UserResponse) {}
rpc UpdateUser(UpdateUserRequest) returns (UserResponse) {}
rpc DeleteUser(DeleteUserRequest) returns (Empty) {}
}
message CreateUserRequest {
string name = 1;
string email = 2;
string password = 3;
}
message GetUserRequest {
string id = 1;
}
message UpdateUserRequest {
string id = 1;
string name = 2;
string email = 3;
string password = 4;
}
message DeleteUserRequest {
string id = 1;
}
message UserResponse {
string id = 1;
string name = 2;
string email = 3;
}
message Empty {}
Step 2: Generate Java Classes from Protocol Buffers:
Next, generate Java classes from the Protocol Buffers definition using the
protoc compiler. Run the following command in the terminal:
protoc --java_out=./src/main/java/ ./user.proto
This generates the necessary Java classes based on the user.proto file.
Step 3: Implement the Microservices:
Create two microservice projects: UserService and AuthenticationService. In
each project, set up the required project structure and dependencies.
In the UserService project, implement the UserService gRPC service by
extending the auto-generated UserServiceGrpc. UserServiceImplBase class.
Implement the gRPC methods according to the defined service interface.
In the AuthenticationService project, implement the AuthenticationService
gRPC service in a similar manner.
Step 4: Build and Package the Microservices:
Use Apache Maven to build and package the microservices into executable JAR
files. Run the following command in each project's root directory:
This will compile the code, run tests, and generate the JAR file for each
microservice.
Step 5: Run the Microservices:
Execute the generated JAR files to run the microservices. In separate
terminal windows, navigate to the target directory of each project and run
the following command:
java -jar <microservice-jar-file>.jar
Step 6: Implement the Client Application:
Create a client application that interacts with the microservices. In the
client application, you will need to add the necessary dependencies for gRPC
and protobuf. Additionally, import the generated Java classes from the
user.proto file.
In the client application, establish a gRPC channel to connect to the
microservices. Create stubs for the UserService and AuthenticationService
using the generated gRPC classes.
You can then use the stubs to make remote procedure calls to the
microservices and perform operations such as creating users, retrieving
users, updating users, and deleting users.
Step 7: Build and Run the Client Application:
Use Apache Maven to build and run the client application. Navigate to the
client application's root directory and run the following command:
This will compile the code and generate an executable JAR file for the
client application.
To run the client application, use the following command:
java -jar <client-application-jar-file>.jar
The client application will establish a connection to the microservices and
perform the specified user management operations.
Considerations and Best Practices
Error Handling
When using gRPC in a microservice application, it's
essential to handle errors effectively. gRPC provides status codes that
indicate the success or failure of a request. Make sure to handle
different types of errors gracefully and provide appropriate error
messages to the client application.
Authentication and Security
In a production environment, it's
crucial to secure the communication between microservices. gRPC supports
various authentication mechanisms, including SSL/TLS and token-based
authentication. Implement authentication and secure the gRPC communication
channels to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of your microservice
application.
Versioning
As your microservice application evolves, you might
need to introduce changes to the gRPC service interfaces. It's important
to plan for versioning and backward compatibility to avoid breaking
existing client applications. Consider using semantic versioning and
implement versioning strategies to handle compatibility across different
versions of your microservices.
Testing
Implement comprehensive unit tests and integration tests
for your microservices. Use tools like JUnit and Mockito to test
individual components and simulate different scenarios. Additionally,
consider using tools like gRPCurl or BloomRPC for manual testing and
debugging of gRPC APIs.
Monitoring and Observability
Implement monitoring and
observability mechanisms in your microservice application. Consider using
tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or Jaeger to collect metrics, monitor
performance, and trace requests. This will help you identify and
troubleshoot issues effectively.
Deployment and Scalability
Design your microservice application
with scalability in mind. Use containerization technologies like Docker
and container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes to deploy and manage
your microservices. Ensure that your microservices can scale horizontally
based on the demand by leveraging features provided by container
orchestration platforms.
In a distributed microservice architecture,
services need to discover and communicate with each other dynamically.
Consider using service discovery mechanisms like Netflix Eureka or
HashiCorp Consul to automate service registration, discovery, and load
balancing.
Conclusion
That's all about how to create a Microservice in Java using gRPC. Building a microservice application using gRPC in Java offers a powerful and
efficient communication mechanism between services. By leveraging the
Protocol Buffers language and the gRPC framework, you can define service
interfaces, generate code, and implement microservices seamlessly.
In this tutorial, we covered the steps involved in creating a microservice
application using gRPC in Java. From defining the gRPC service and message
types to implementing the microservices and client application, you learned
how to leverage gRPC to facilitate communication and build scalable
microservice architectures.
Remember that this tutorial provides a basic example to help you understand
the process. In real-world scenarios, you would need to consider aspects
such as error handling, authentication, and deployment strategies. However,
the fundamental principles and techniques discussed here will serve as a
solid foundation for developing robust microservice applications using gRPC
in Java.
By harnessing the power of gRPC, you can unlock the full potential of
microservices and build flexible, scalable, and efficient distributed
systems.
Other
Java Microservices articles and tutorials you may like



No comments:
Post a Comment
Feel free to comment, ask questions if you have any doubt.