Hello guys, if you are wondering how to secure your Microservices, like put authentication and authorization then you have come to the right place. Security is a critical aspect of any software architecture, and microservices architecture is no exception. With its distributed and decentralized nature, microservices architecture presents unique security challenges that must be addressed to ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of the system.In this article, we will discuss some best practices for implementing security in microservices architecture.
How To Implement Security in Microservices Architecture
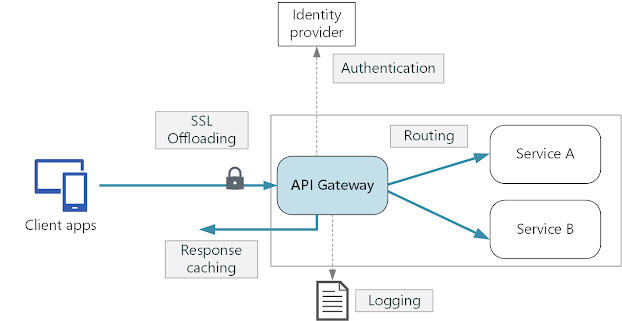
So, what are we waiting for let's deep dive on securing Microservices. we will start with Authentication and Authorization first:1. Authentication and Authorization
Authentication
and authorization are fundamental to securing any system. In a
microservices architecture, each service must have its own
authentication and authorization mechanism. This allows each service to
control access to its resources and ensure that only authorized users
can access them.
There are various authentication and
authorization mechanisms that can be used in microservices architecture,
such as OAuth 2.0, JSON Web Tokens (JWT), and OpenID Connect. These
mechanisms provide a standardized way of handling authentication and
authorization across services.
2. Use of Secure Communication
Communication
between microservices should be secure to prevent unauthorized access
or modification of data. The use of HTTPS and TLS protocols can provide
secure communication between services. Encryption and decryption of data
transmitted between services can ensure confidentiality.
3. Secure Data Storage
Data
storage is another important aspect of security in microservices
architecture. Each service should have its own database or data store,
and access to the database should be restricted to authorized users.
Data should be encrypted both in transit and at rest to ensure its
confidentiality.
4. Secure Service-to-Service Communication
Service-to-service
communication is a key aspect of microservices architecture. However,
it can also be a point of vulnerability if not secured properly. One way
to secure service-to-service communication is to use mutual TLS (mTLS).
mTLS ensures that only trusted services can communicate with each
other.
5. Monitoring and Logging
Monitoring
and logging are critical to detecting and responding to security
incidents in a timely manner. Each service should have its own logging
and monitoring system to track and detect security incidents. This can
include tracking failed login attempts, access to sensitive data, and
unauthorized access attempts.
6. Regular Security Audits
Regular
security audits should be performed to ensure that the system is secure
and compliant with industry standards and regulations. This can include
penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and code review.
7. Continuous Security Improvement
Security
in microservices architecture is an ongoing process. It is important to
continuously improve and update security measures as new threats and
vulnerabilities are discovered. This can include updating software,
implementing new security measures, and providing security training for
developers and users.
8. Limiting Access to Sensitive Information
Access
to sensitive information should be restricted to authorized personnel
only. This can include personally identifiable information (PII),
financial data, or other confidential information. Access control
mechanisms such as role-based access control (RBAC) or attribute-based
access control (ABAC) can be used to limit access to sensitive
information.
9. Secure Deployment and Configuration
Deployment
and configuration of microservices should be done in a secure manner to
prevent vulnerabilities from being introduced. This can include using
secure deployment pipelines, hardening the operating system, and
ensuring that all configurations are securely stored and protected.
10. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity Planning
Disaster
recovery and business continuity planning are essential for maintaining
the availability of the system in the event of a security incident or
disaster. This can include backup and recovery procedures, redundant
systems, and failover mechanisms.
11. Security Training for Developers and Users
Developers
and users should receive training on security best practices to ensure
that they are aware of the risks and vulnerabilities associated with the
system. This can include training on secure coding practices, password
management, and how to identify and respond to security incidents.
12. Compliance with Industry Standards and Regulations
Microservices
architecture must comply with industry standards and regulations such
as PCI-DSS, HIPAA, or GDPR. Compliance with these standards and
regulations can help ensure that the system is secure and meets the
necessary requirements for handling sensitive data.
13. Use of Containerization and Orchestration
Containerization
and orchestration tools such as Docker and Kubernetes can provide
additional security benefits in microservices architecture. Containers
can be isolated from each other, providing an additional layer of
security, and orchestration tools can help ensure that containers are
deployed securely and efficiently.
14. Implementing Defense in Depth
Defense
in depth is an approach to security that involves implementing multiple
layers of security measures. This can include firewalls, intrusion
detection and prevention systems, and antivirus software. Implementing
defense in depth can help ensure that even if one security measure is
compromised, there are other measures in place to prevent an attack.
15. Threat Modeling
Threat
modeling is the process of identifying potential security threats and
vulnerabilities and developing countermeasures to mitigate them. In
microservices architecture, threat modeling can help identify potential
attack vectors and vulnerabilities in the system, allowing developers to
develop appropriate security measures.
16. Zero-Trust Security Model
The
zero-trust security model is an approach to security that assumes that
all users, devices, and services are untrusted and must be authenticated
and authorized before access is granted. This approach can provide an
additional layer of security in microservices architecture, where
multiple services and devices may be accessing each other.
17. Implementing Immutable Infrastructure
Immutable
infrastructure is an approach to infrastructure management that
involves creating a configuration that cannot be modified. This can help
prevent configuration drift and ensure that the system is always
running in a known, secure state.
18. Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD)
Continuous
integration and deployment (CI/CD) is a development practice that
involves automating the process of building, testing, and deploying code
changes. This can help ensure that changes are thoroughly tested and
deployed securely and efficiently.
19. Secure Third-Party Integration
Many
microservices architectures rely on third-party services for various
functions. It is important to ensure that these services are secure and
do not introduce vulnerabilities into the system. This can include
conducting security assessments of third-party services and ensuring
that they comply with industry standards and regulations.
20. Regular Security Training and Awareness
Regular
security training and awareness programs can help ensure that all
stakeholders in the microservices architecture are aware of the risks
and vulnerabilities associated with the system. This can include
training on phishing awareness, password management, and incident
response.
Conclusion
By
implementing these best practices for security in microservices
architecture, organizations can help ensure the integrity,
confidentiality, and availability of their systems. However, it is
important to keep in mind that security is an ongoing process that
requires continuous improvement and monitoring to stay ahead of evolving
threats and vulnerabilities.
In conclusion,
security is a critical aspect of microservices architecture.
Implementing security best practices such as authentication and
authorization, secure communication, secure data storage, secure
service-to-service communication, monitoring and logging, regular
security audits, and continuous security improvement can help ensure the
integrity, confidentiality, and availability of the system. By
following these best practices, organizations can reduce the risk of
security incidents and protect their assets from unauthorized access or
modification.
.jpg)

No comments:
Post a Comment
Feel free to comment, ask questions if you have any doubt.