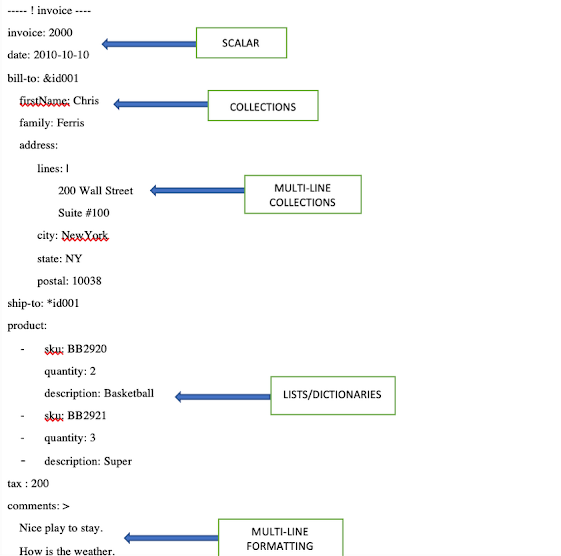
YAML syntax
YAML derive many features from a popular programming language such as XML, HTML, C, and other. It reminds you of python when it comes to indentation. Like python, we can’t use braces, brackets, or any sort of closing tags in it. The extension we use for defining YAML document is .yml or .yamlAn Example of YAML document:
The below written YAML configurations demonstrate a student’s school record. It is saved with .yml or .yaml extension.
Student record sample
name: John
school: X high school
age: 18
registered_since: 2008
interest:
- Football
- Hockey
- Tennis
languages:
english: Fluent
spanish: Conversational
chinese : BasicWhy do We Use YAML?
Even though YAML can be used with some programming languages but the most common and widely appreciated use is to create configuration files. But a question might appear in your mind why leave JSON in the first place?Although they can usually be used interchangeably, it is advised that configuration files be written in YAML rather than JSON because it is easier to understand and more user-friendly. Another reasonable advantage that YAML offer is it allows source control tools, such as GitHub, to keep track of and perform auditing of modifications.
Let’s shed some light on the difference between YAML and properties files as these are frequently used in Spring Boot Applications to hold configurations.
These configurations are later referenced while making a connection with the database, reading properties such as username, password, database connection URL, dialect, on which port the application will run, and whether to log SQL query in the console, it can also assist you in defining public routes, CORS, and many more configurations.
Difference between YAML vs Properties syntax?
Below written code snippet represents application.properties syntax.student.name = some-name
student.age = some-age
student.school = name-of-school
student.favourite-subject = subject-name
student.hobbies = student-hobby-1, student-hobby-2, student-hobby-3, and so onYou might have noticed we have to repeat the student’s alias every time a new property is desired, a better way to use the YAML file.
The above code snippet can be rewritten using YAML syntax.
Student:
name: some-name
age: some-age
school: name-of-school
favourite-subject: subject-name
hobbies:
- student-hobby-1
- student-hobby-2
- student-hobby-3
- and so onLet’s take a look at another example
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/funGun
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=log500900500
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect
spring:
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update
show-sql: true
database-platform: org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/funGun
username: root
password: log500900500
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver Hope the above syntax will clarify, how YAML can save time by reducing the repetitive code. So far we have seen what are YAML files, why it is used in the first place, and why many developers prefer them over properties file.
How to define List and Map in YAML? Example
It's time to start learning how to create lists and maps in YAML files. From the code below we can see how to declare a list and a map in a YAML file. Additionally, the program will also demonstrate how to use the Spring Boot application to access the map and list attributes from the YAML file.
Build.gradle
plugins {
id 'java'
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '3.0.1'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.1.0'
}
group = 'com.usama'
version = '0.0.1-SNAPSHOT'
sourceCompatibility = '17'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
implementation 'org.projectlombok:lombok:1.18.22'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa'
implementation 'mysql:mysql-connector-java:5.1.6'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
}
tasks.named('test') {
useJUnitPlatform()
}Declaring a List in YAML file
myapp:
shop:
cricket:
- bat
- ball
- wickets
- helmet
- pads
- gloves
- sun-glass
- shoes
- thigh-guards
- elbow-guards
- arm-guards
- chest-guard
electronic:
- air-purifier
- air-conditioner
- backup-charger
- blender
- bluetooth-speakerDeclaring a Map in YAML file
shop-user:
-
username: john-smith
email: john@****.com
password: pass***
-
username: peter-gom
email: peter@****.com
password: pass***
-
username: maxwell
email: maxwell@****.com
password: pass***
Mapping YAML to Java List using Spring Boot
ShopProperties.java
This class will act as a container for holding YAML properties. Here we have mainly two properties
Cricket shop item
Electronic shop items
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties("myapp.shop")
public class ShopProperties{
List<String> cricket;
List<String> electronic;
Map<String,Object> shopUser;
public List<String> getCricket() {
return cricket;
}
public List<String> getElectronic() {
return electronic;
}
public Map<String, Object> getShopUser() {
return shopUser;
}
public void setShopUser(Map<String, Object> shopUser) {
this.shopUser = shopUser;
}
public void setCricket(List<String> cricket) {
this.cricket = cricket;
}
public void setElectronic(List<String> electronic) {
this.electronic = electronic;
}
}REST end-point to access the defined List and Map
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/shop")
public class ShopController {
@Autowired
ShopProperties shopProperties;
@RequestMapping("/cricket/items")
public ResponseEntity<?> getCricketItems(){
return new ResponseEntity<>(shopProperties.getCricket(), HttpStatus.OK);
}
@RequestMapping("/electronic/items")
public ResponseEntity<?> getElectronicItems(){
return new ResponseEntity<>(shopProperties.getElectronic(), HttpStatus.OK);
}
@RequestMapping("/shop-users")
public ResponseEntity<?> getShopUsers(){
return new ResponseEntity<>(shopProperties.getShopUser(), HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
Accessing the List Items using REST end-points
GET /api/v1/shop/cricket/items
[
"bat",
"ball",
"wickets",
"helmet",
"pads",
"gloves",
"sun-glass",
"shoes",
"thigh-guards",
"elbow-guards",
"arm-guards",
"chest-guard"
]As you can see we can fetch the list we specified in the application.yml file. Now let’s try to access electronic items.
GET /api/v1/shop/electronic/items
[
"air-purifier","
air-conditioner",
"backup-charger",
"blender",
"bluetooth-speaker"
]
By accessing the above end-point, we will be able to fetch the electronic shop items specified in the application.yml file.
Accessing the Map entities using REST end-points
GET /api/v1/shop/shop-usersThe above endpoint will return list of key value pairs that carry shop users data.
{
"0": {
"username": "john-smith",
"email": "john@****.com",
"password": "pass***"
},
"1": {
"username": "peter-gom",
"email": "peter@****.com",
"password": "pass***"
},
"2": {
"username": "maxwell",
"email": "maxwell@****.com",
"password": "pass***"
}
}That's all about what is YAML and how to declare list and Map in YAML. With this, our article is at its conclusion. This brief essay aims to explain what YAML files are and why they are used so frequently to write application configurations. We also conducted a brief comparison regarding the syntax of properties and YAML files.
Moving ahead, we discovered how to specify lists and maps in a YAML file. Finally, we build a Spring-based REST API to map YAML configurations into java objects. Hope this clarifies our understanding related to the YAML file.

No comments:
Post a Comment
Feel free to comment, ask questions if you have any doubt.