The use of a window function does not cause rows to become grouped into a single output row. the rows retain their separate identities. Behind the scenes, the window function is able to access more than just the current row of the query result.
How to use Window Function in SQL?
A window function can also be called an analytic function, A window is a function that uses values from one or multiple rows to return a value for each row. (This contrasts with aggregate functions, which return a single value for multiple rows.)
Window functions have an OVER clause; any function without an OVER clause is not a window function, but it can only be an aggregate or single-row (scalar) function.
Let us say we have an employee table for instance.
EMPLOYEE TABLE
name department age salary
Grace Rolli operations 21 150,000
Cyndi Lo operations 20 200,000
Wilms cole maintenance 25 100,000
Alfred Toni maintenance 19 97,000
John Smith sales 23 50,000
Chukwu Dan sales 27 75,000
So here is another practical code example. our employee table above, now we want to write a window function for it in SQL.
- SELECT name, age, department, salary,
- AVERAGE(Salary) OVER( PARTITION BY Department ORDER BY Age)
- AS Avg_Salary
- FROM employee;
Now, what this query is saying is that. name column, age column, department, and salary column should be selected from the employee table(check line 4). In line 2, an aggregate function "average" was performed on the salary column and after that has been done, what happens under the hood is that it creates another column as Avg_salary and puts each average salary of each employee in its appropriate rows.
The "Over" keyword which is at line two is what makes it a window function, now let us deal with that. You would see that inside the parenthesis of the "over" function there are lines of command to be carried out there.
It is simply saying that function is partitioned by department and order by age. (There may be different kinds of things to do here, it all depends on what you what to do).
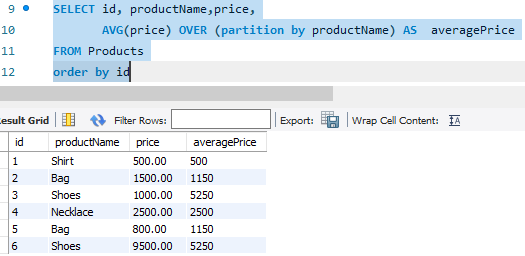 |
| Fig 1.0 A visual representation of how window function works. |
This partition keyword groups whatever you have specified into parts. In our case, department. All departments that are the same would be seen together. if we have 5 A's departments you would see them together you won't see any B's departments in between.
After that now comes another set of similar departments. and so on and so forth, That is for partitioning." Order By" sorts it accordingly. and by default, it is in ascending order. so, After departments are partitioned then it begins to sort it according to each partitioned department.
Below is what it looks like:
name department age salary Avg_Salary
Alfred Toni maintenance 19 90,000 45,000
Wilms cole maintenance 25 100,000 50,000
Cyndi Lo operations 20 200,000 100,0000
Grace Rolli operations 21 150,000 75,000
John Smith sales 23 50,000 25,000
Chukwu Dan sales 27 70,000 35,000
Windows functions can access rows. It enables a sub-division or splitting into rows and They still maintain their different identities.
Types or Class of Windows functions
There are three classes or categories of windows Functions:
- Ranking
- Value
- Aggregation
We shall be taking this one after the other in explanation
Ranking: The name “Ranking” is suggestive. When you hear ranking it means it has to do with the ranking or the top-leading information that is associated with the rows and columns. It displays the ranking information.
Value: Value gives you whatever that is assigned, which correlates with each partition
Aggregation: It shows the aggregate values from numerical columns.
Conclusively, You may imagine, when do you need to use a window function?
A window function is used when you need to perform some calculations and you need the result of the calculation on each row.
- 5 Free Courses to learn T-SQL and SQL Server for Beginners (Courses)
- Difference between the Unique and Primary keys in the table? (answer)
- 5 Courses to learn Database and SQL Better (courses)
- The real difference between WHERE and HAVING clause in SQL? (answer)
- 5 Free Courses to learn Database and SQL (free courses)
- Difference between clustered and non-clustered indexes in SQL? (answer)
- Difference between Primary and Candidate key in the table? (answer)
- 5 Free Courses to learn Oracle and SQL Server? (courses)
- 5 Courses to learn Oracle and Microsoft SQL Server database (courses)
- Difference between Self and Equi Join in SQL? (answer)
- How to join three tables in one single SQL query (solution)
- Write a SQL query to find all table names on a database in MySQL (solution)
- 4 Free Books to learn Microsoft SQL Server database (books)
- How do you find the duplicate rows in a table on a database? (solution)
- 5 Free Courses to learn T-SQL and SQL Server for Beginners (Courses)
- Top 5 Courses to learn Microsoft SQL Server in-depth (courses)
- How to migrate SQL queries from Oracle to SQL Server? (answer)
- Top 5 Websites to learn SQL online for FREE? (websites)
- What is the difference between UNION and UNION ALL in SQL? (answer)
- Write a SQL query to copy or backup a table in MySQL (solution)
- Top 5 Websites to learn SQL online for FREE? (resource)
- Difference between Primary and Foreign keys in the table? (answer)
No comments:
Post a Comment
Feel free to comment, ask questions if you have any doubt.