Hello guys, if you are wondering what is difference between HashMap, TreeMap and LinkedHashMap in Java and when to use HashMap, TreeMap and LinkedHashMap in Java then you are at the right place. Earlier, I have shared difference between HashSet, TreeSet, and LinkedHashSet and in this article, I will explain the difference between these three common Map implementation HashMsp, TreeMap, and LinkedHashMap. Though all three classes like HashMap, LinkedHashMap and TreeMap are
implementation of java.util.Map interface, there is some functionality difference
between them. Perhaps most notable difference between them comes from their
iteration order. HashMap makes absolute no guarantee about in which order you
can iterate their keys, any application depending upon iteration order of
HashMap is fragile, because it can change anytime. In fact, in Java 7,
iteration order of HashMap is different than Java 6.
On the other hand TreeMap is a SoretedMap and keeps their key in particular sorted order, enforced by
either natural order of keys or Comparator instance provided during
construction of TreeMap.
The third Map, LinkedHashMap can maintain its keys in two order, either
insertion order (on which those keys are inserted) or access order (on which
they are accessed). By default, LinkedHashMap keeps keys in insertion order, I mean in the order you will add keys into Map.
If you want to maintain access order, just provide true to access order
boolean parameter.
Another crucial difference between HashMap, TreeMap and LinkedHashMap comes
from their performance for common operations like get(), put(), remove() and
containsKey(); both HashMan and LinkedHashMap provides O(1) performance, while
TreeMap provides O(log(n)), so it's slightly slow compared to other two.
This is actually the cost you need to pay to keep keys in their sorting order.
Apart from these major differences, we will learn couple of more in next
section.
Difference between HashMap, LinkedHashMap and TreeMap in Java
Here are some important difference between TreeMap, LinkedHashMap, and HashMap
in Java on point format
1. Order of Elements
HashMap doesn't maintain any order, TreeMap keeps all elements in sorted order, specified by Comparator or object's natural order defined by Comparable. LinkedHashMap keeps elements in the same order they are inserted into map.2. Performance
HashMap gives best performance because there is no overhead, TreeMap gives
slower performance because every time you add or remove mapping , it need to
sort the whole map. LinkedHashMap gives performance in between,
3. Null keys and values
HashMap allows only one null keys and allows multiple null value, but TreeMap doesn't allow
null key. LinkedHashMap allows null key.
Iterator of all map are fail-fast in nature. Which means all HashMap, TreeMap, and LinkedHashMap have fail fast iterator, so no difference in this point.
5. Internal implementation
HashMap is internally based upon hash table data structure, TreeMap is based
upon Red Black Tree and LinkedHashMap uses doubly linked list to keep elements
in the same order they are inserted.
6. Synchronization
None of these map are synchronized.
7. Usage
LinkedHashMap also provides a great starting point for creating a Cache object by overriding the removeEldestEntry() method. This lets you create a Cache object that can expire data using some criteria that you define. For example, you can use this method to create a LRU Cache in Java.
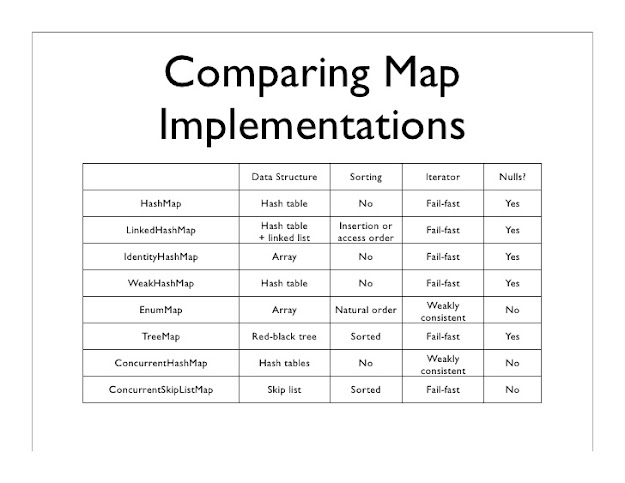
And, here is a nice table of all the difference between HashMap,
LinkedHashMap, Hashtable, and TreeMap in Java
That's all about
difference between HashMap, LinkedHashMap and TreeMap in Java. These
differences includes both functional and non-functional differences between
them. If you know them well, it will be easy for you to choose right kind of
Map depending upon situation.
If you forget everything then just remember that HashMap is your general
purpose Map, whenever you need a hash table data structure just use it.
TreeMap is your sorted Map which keep keys in sorted order like stock exchange
keep order sorted in time and price priority, and LinkedHashMap maintains
insertion order, the order on which elements was added. You can use it
implement LRU cache in Java.
Other Java 8 tutorials you may like:
- How to use compute() and computeIfPresent() in Java Map
- 5 Courses to learn Java 8 in-depth
- How to join String in Java 8
- 10 Example of Stream class in Java
- How to sort HashMap by values in Java 8?
- 10 examples of Optional in Java 8?
- How to sort the map by keys in Java 8?
- 5 Books to Learn Java 8 from Scratch
- How to use the filter method in Java 8
- 10 Java 8 Stream Interview Questions with Answers
- How to use the forEach method in Java 8
- 10 Example of Optional class in Java
Thanks for reading this article so far. If you like this difference between
TreeMap, HashMap and LinkedHashMap in Java then please share with your
friends and colleagues, if you have any questions or doubt then please drop
a comment.
P. S. - If you are new to Java world and want to understand Java Collection framework in depth along with all data structure Java provides then I also suggest you to checkout this list of best Java collections and Stream courses where you will find best courses to learn Java Collections in depth from Udemy, Pluralsight, Educative, and Coursera.

Please correct "Hashmap does allow one null key"
ReplyDeleteYes, that's correct, HashMap does allow only one null key and it stored at zero location on array. Thanks for pointing out, its corrected now.
Delete